Disclaimer: This guide is for emergency situations when immediate professional medical care is not available. Always call emergency services (911) first. This information is not a substitute for professional medical treatment.
Immediate Actions
1. Ensure Safety First
- Check the scene for potential dangers
- Protect yourself (wear gloves if available)
- Only proceed if safe to do so
2. Call for Emergency Help
- Dial emergency services immediately
- Put phone on speaker for hands-free guidance
- State location and nature of emergency clearly
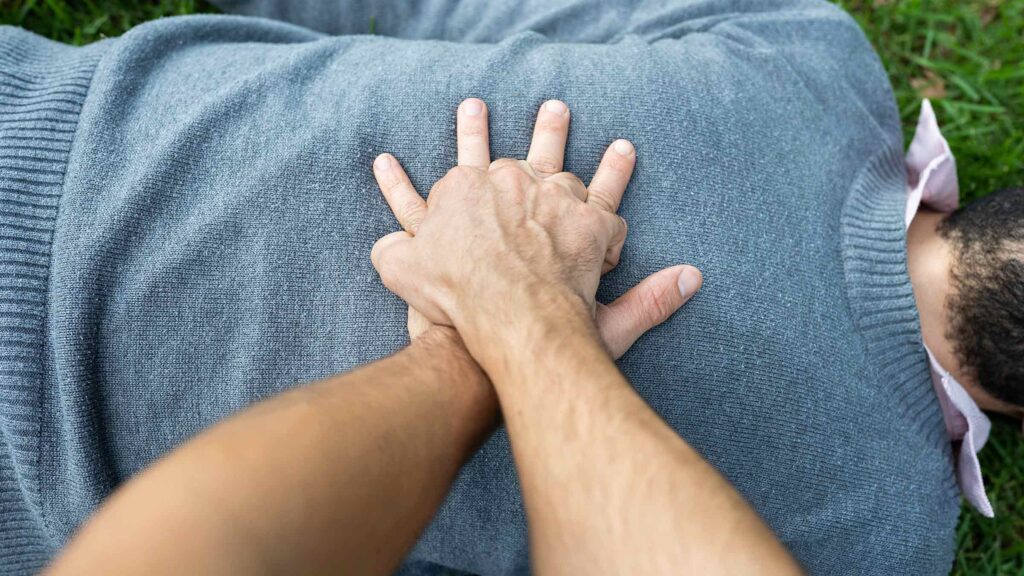
3. Check Vital Signs
- Check consciousness
- Monitor breathing
- Check pulse
- Look for signs of shock
Major Trauma Types and Immediate Response
Severe Bleeding
- Apply direct pressure with clean cloth/gauze
- Elevate injured area if possible
- Use pressure points if necessary
- Apply tourniquet only as last resort
Head Trauma
- Keep person still
- Monitor consciousness
- Clear airway if necessary
- Don’t move neck if spinal injury suspected
Chest Wounds
- Seal open chest wounds with plastic
- Leave one corner unsealed
- Monitor breathing
- Keep person calm
Broken Bones
- Immobilize the area
- Apply cold packs
- Check circulation
- Don’t attempt to realign
Signs of Critical Condition
Watch for:
- Irregular breathing
- Bluish skin color
- Rapid pulse
- Cold, clammy skin
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
Important Don’ts
- Don’t remove embedded objects
- Don’t give food or drink
- Don’t move the person unnecessarily
- Don’t leave the person alone
- Don’t panic
Preparation Tips
Keep these supplies readily available:
- Clean gauze and bandages
- Sterile gloves
- Scissors
- Clean cloths
- First aid tape
- Emergency contact numbers
When to Expect Professional Help
- Urban areas: 5-10 minutes
- Rural areas: 15-30 minutes
- Remote areas: 30+ minutes
After Help Arrives
- Brief emergency responders
- Share any relevant medical history
- Describe what happened
- List any actions taken
Remember: Your primary goal is to keep the person stable until professional help arrives. Stay calm and focused.